When considering the production of undercarriage parts for excavators & bulldozer, I often find it challenging to align our quality control processes with specific client needs. The importance of crafting standards that cater to individual product requirements cannot be overstated.
Understanding client-specific requirements is crucial in developing AQL (Acceptance Quality Limit) 1 sampling standards and inspection items that meet undercarriage parts for excavators & bulldozer’ unique demands. Customizing these processes not only aligns with critical-to-quality features but also ensures consistent high quality.
Our customers depend on a robust standard that guarantees their needs are met. Ensuring that every part meets this standard is key. But how do we ensure these standards are flexible enough for different components?
Will You Align AQL Levels with My Critical-to-Quality Features for My Undercarriage Parts for excavators & bulldozer?
Sometimes, I’ve faced situations where balancing critical-to-quality (CTQ) features 2 with acceptable quality limits seemed like walking a tightrope. It’s a constant battle between ensuring quality and maintaining efficiency.
Yes, aligning AQL levels with critical-to-quality features is possible through collaborative discussions and evaluations. This helps set quality standards reflective of the part’s importance and the potential impact on machinery performance.
Implementing clear AQL levels is essential for achieving defect-free parts that fulfill functional requirements. Here’s how these considerations affect your components:
AQL Levels Matrix
| Feature Type | Critical Defects | Major Defects | Minor Defects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Safety Elements | AQL 0 | AQL 1.0 | AQL 3.0 |
| Functional Parts | AQL 1.0 | AQL 2.5 | AQL 4.0 |
| Cosmetic Aspects | AQL 2.5 | AQL 4.0 | AQL 5.0 |
Customizing AQL levels aids in isolating and addressing potential failures before they reach the client. Regular evaluations help adapt these standards as technology and customer needs evolve. Additionally, leveraging feedback from field usage 3 informs any necessary adjustments.
Can I Set Different AQLs for Appearance vs Dimensions in My Parts for My Undercarriage Parts for excavators & bulldozer?
Balancing the visual appeal of undercarriage parts for excavators & bulldozer with dimensional accuracy is no easy task. Consistency in one often feels like sacrificing the other.
Certainly, varying AQLs for appearance versus dimensions is practical and enhances focus on what’s essential for each part. This flexibility allows for a precision approach, tailoring inspections to specific needs.
Focusing on Appearance vs Dimensions
Splitting focus between appearance and dimensional specifics requires distinct evaluation processes for effective quality control results. Here’s what this looks like:
Appearance Considerations
- Visual Inspections: Regular checks ensure cosmetic consistency.
- Marking Standards: Branding and part identification needs visual clarity.
- Surface Treatments: Assess paint or coating applications for uniformity.
Dimension Specifics
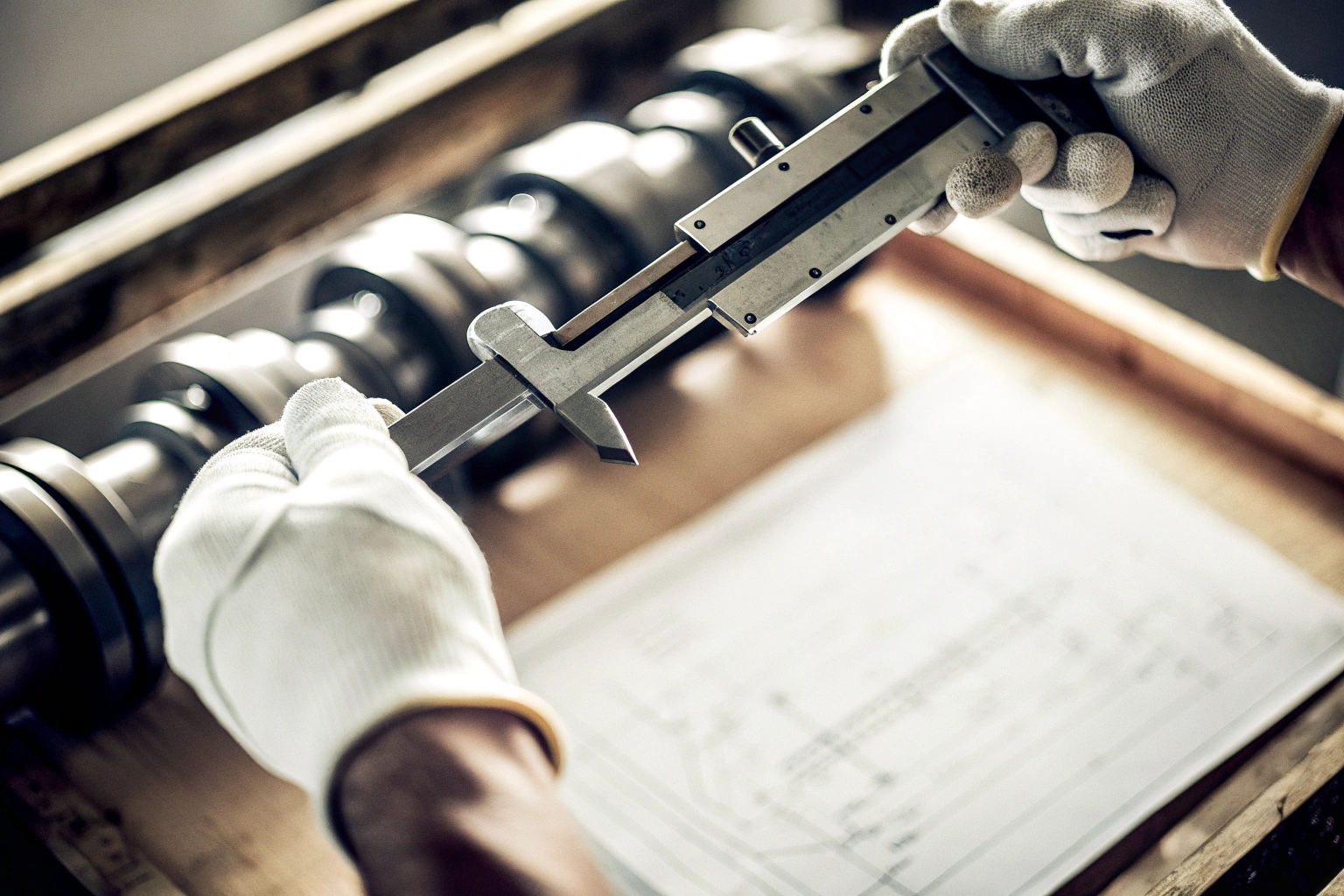
- Measurement Tools: Calipers and micrometers 4 ensure precision.
- Tolerance Levels: Strict adherence to specified tolerances.
- Function Checks: Test-fit checks confirm functional integrity.
Regularly training quality teams ensure these variances are understood, leading to consistent production results. This approach is vital in long-term client satisfaction and reputation-building.
Navigating defect standards without clear guidance feels like wandering through a forest without a map. It’s vital for the teams to have concrete references.
Providing defect catalogs and visual standards enhances the understanding and identification of defects during the inspection. This aids in promoting consistent quality inspection results.
Establishing clear guidelines for common defects 5 and visual expectations ensures our team is on the same page. Here’s a breakdown:
Defect Categories
- Critical Defects: Impact safety and functionality.
- Major Defects: Affect usability and efficiency.
- Minor Defects: Cosmetic or minor functional impacts.
Visual Guides
- Sample References: Use example images for easy identification.
- Defect Descriptions: Detailed text outlines for standards.
- Measuring Tools: Visual aids for measurement checks.
With such resources, inspectors can confidently execute assessments, contributing to the ongoing quality assurance processes. Investing time in these resources pays dividends in quality confidence.
Can You Train My Inspectors on Your AQL Process Remotely for My Undercarriage Parts for excavators & bulldozer?
Access to remote training often seems out of reach but bridging this gap is essential for global operations. In today’s digital world, making training accessible remotely has become indispensable.
Yes, comprehensive remote training on an AQL process equips your inspectors with the necessary skills to uphold standards without geographical barriers impacting learning.
Remote Training Modules
- Interactive Sessions: Live demonstrations and real-time discussion forums.
- Digital Documentation: Access to guides and resources.
- Progress Evaluations: Regular assessments ensure concept comprehension.
- Feedback Loops: Continuous dialogue to address emerging questions.
Having this flexibility not only supports existing teams but also integrates new team members seamlessly. It’s a modern tool in maintaining competitive edge in quality assurance.
Conclusion
Customizing inspection and AQL standards ensures unmatched quality and client satisfaction in providing undercarriage parts for excavators & bulldozer. Consistent evaluation and adaptation to satisfy ongoing requirements seal the path to success.
Footnotes
1. AQL helps in defining acceptable defect levels during inspections. ↩︎
2. CTQ outlines customer priorities influencing quality criteria. ↩︎
3. Field usage data assists in refining product standards. ↩︎
4. Precision tools necessary for accurate dimensional inspections. ↩︎
5. Common defects guide ensures uniform standards application. ↩︎