Handling different specifications can be complicated, especially when dealing with distinct metric and imperial systems 1. I often hear concerns from customers about compatibility across equipment sourced globally.
A reliable undercarriage parts for excavators & bulldozer supplier should offer parts in both imperial and metric specifications to cater to diverse market needs. It is common to find products labeled with "inch" or "mm" for easy identification. This ensures compatibility with varying machinery requirements 2 across global markets.
Understanding the nuances of metric and imperial specifications is vital. Suppliers who serve international customers are more likely to offer both standards and may even provide custom solutions. Websites often include filters for specification types, indicative of a supplier’s capability in handling diverse systems. Being aware of these details can aid in making informed purchasing decisions.
How do you prevent errors when converting between metric and imperial drawings?
Preventing conversion errors is tricky, a source of headaches for many vendors. Personally, I’ve encountered issues where slight miscalculations cause significant project delays.
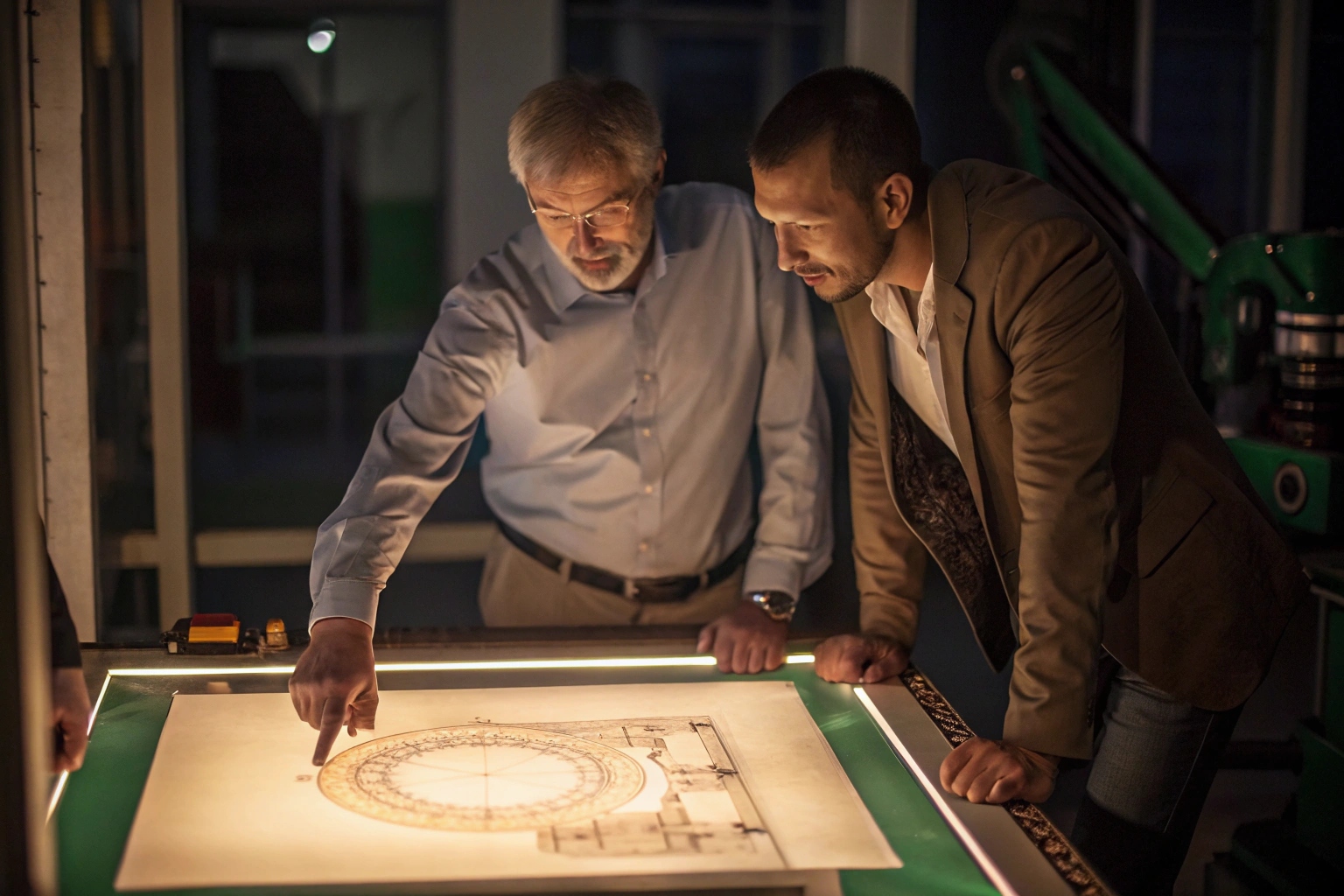
It’s crucial to convert measurements accurately to prevent errors. Suppliers may employ detailed conversion charts and tools 3 to ensure precision when switching between metric and imperial systems. Accurate conversion supports seamless integration and compatibility across diverse machinery setups.
Errors can arise when converting between metric and imperial specifications. To mitigate this, many suppliers incorporate robust systems to facilitate accurate conversions. Charts or software may be used to ensure precise consistency between systems. Furthermore, personnel trained to interpret US-based drawings 4 ensure reliability in conversion tasks.
Conversion Methods
-
Manual References: Some suppliers use traditional conversion charts to convert dimensions by hand. Accuracy relies heavily on human calculations.
-
Software Solutions: Advanced suppliers may use specialized software that automates conversions 5, reducing the potential for human errors.
-
Error Prevention Strategies: Training programs for staff can enhance skills in handling drawings and measurements.
| Conversion Type | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Manual Charts | Simplicity | Prone to human error |
| Software | Accuracy | May require updates |
| Staff Training | Skill improvement | Time-consuming |
Do you stock or manufacture hardware (bolts, nuts) in both systems?
The complexity of stocking hardware in dual systems often leads to inventory management issues. Personally, I’ve witnessed suppliers struggle with space constraints.
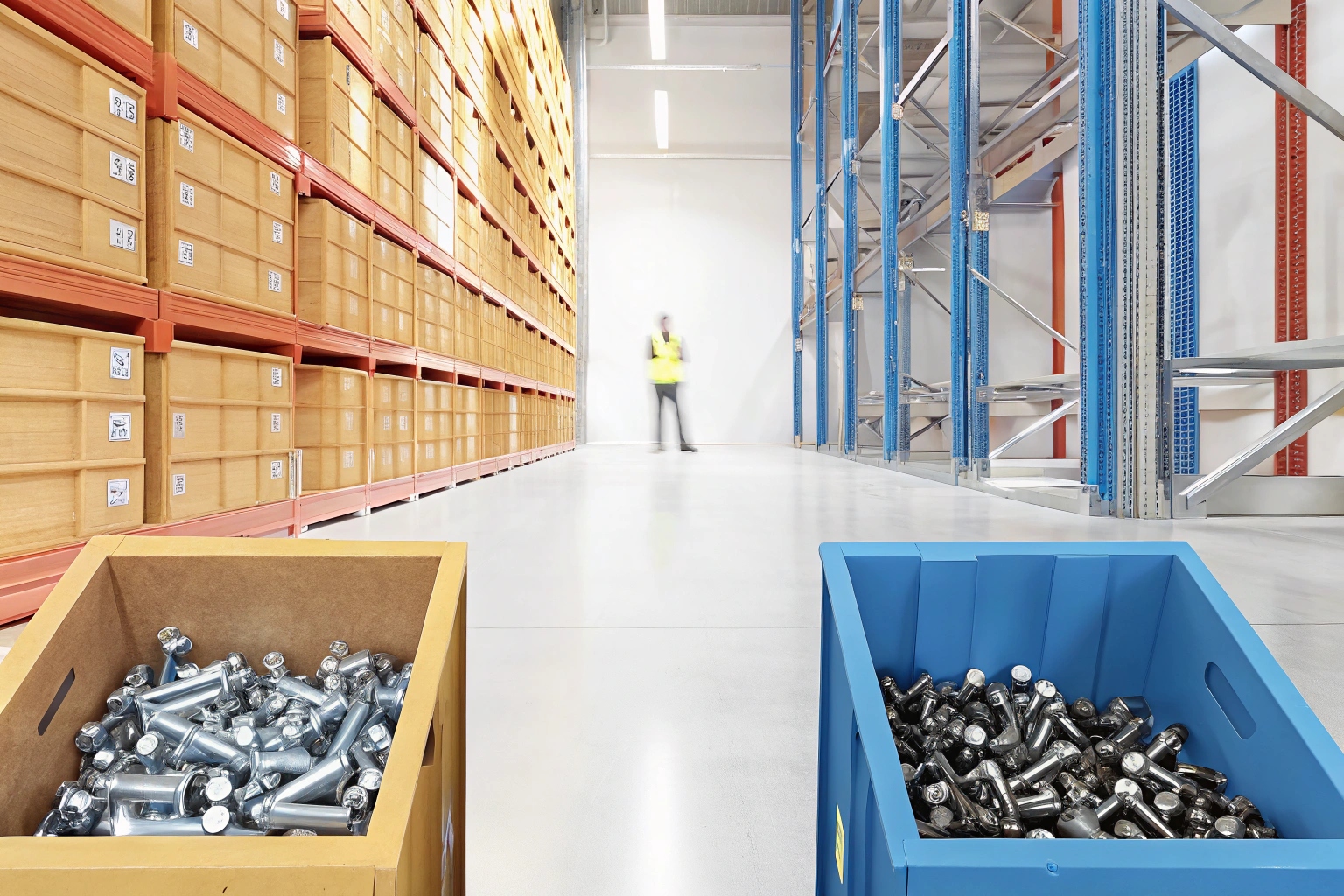
Manufacturers should stock both metric and imperial bolts and nuts 6 to meet global demand. As these are not interchangeable, precise threading and pitch measurements are crucial. Suppliers who handle both systems typically employ efficient inventory management controls 7 to accommodate customer requirements.
Stocking hardware in both metric and imperial systems can be challenging. Suppliers need to maintain sufficient inventory levels to prevent shortage issues. This includes organizing stock based on thread dimensions and ensuring compatibility with existing machinery. OEM specifications 8 often guide the use of specific bolts and nuts, and conversions are not straightforward due to thread variations.
Inventory Management for Hardware
- Diverse Stocking: Suppliers carry both metric and imperial fasteners to cater to different machine specifications.
- Thread Compatibility: Ensuring thread compatibility with OEM requirements is vital for seamless installation.
- Supply Chain Stability: Robust supply chain systems help prevent inventory shortages and ensure timely delivery.
| System Type | Compatibility | Stocking Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Metric | International | Variety requirements |
| Imperial | U.S.-based | Limited international applicability |
Are your technical staff fluent in reading US-based (imperial) engineering drawings?
Training teams to decipher varied specifications is tough. I’ve seen suppliers hire dual-system experts to ensure flawless interpretation.
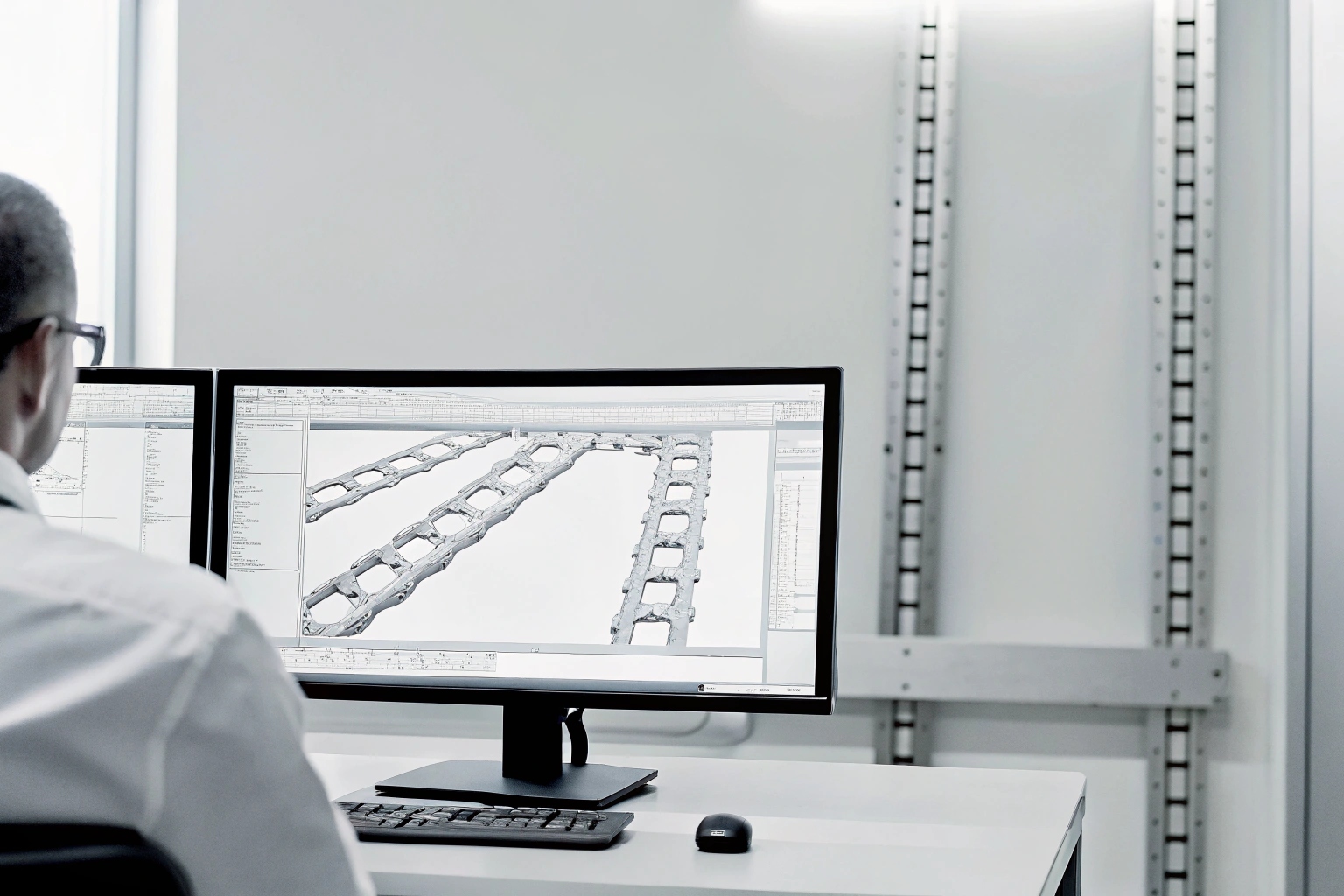
Technical staff should be adept at reading both metric and imperial engineering drawings 9 for precision. This fluency guarantees accurate production and compliance with OEM requirements, minimizing risks of miscommunication or product defects.
Engineering drawings require precise interpretation, which demands staff proficiency in both metric and imperial systems. Suppliers often train their personnel to ensure fluency in reading US-based drawings. This proficiency is vital for maintaining product quality and ensuring that component specifications align with machinery requirements.
Importance of Technical Fluency
-
Cross-Training: Providers might implement cross-training programs to bolster skills in interpreting diverse specifications.
-
Quality Assurance: Skilled technical staff contribute to superior product quality through adept drawing interpretations.
-
Communication Efficiency: Fluent staff reduce communication errors with international clients through clear specification understandings.
What is your cross-reference system for metric and imperial equivalent parts?
Cross-referencing equivalent parts entail complexities, a meticulous process. Experienced suppliers often develop automated systems for efficiency.
Suppliers must maintain cross-reference systems 10 to ensure accurate matching of metric and imperial parts. Inventory systems often require integration capabilities to seamlessly correlate equivalent components, facilitating swift transitions between measurement standards.
Cross-referencing between metric and imperial parts can be complex. Suppliers use robust systems to track part equivalencies and ensure accuracy in order processing. This often includes comprehensive databases that correlate metric and imperial specifications with OEM part numbers for diverse customer needs.
Cross-Reference Techniques
- Database Systems: Suppliers maintain extensive databases linking equivalent part numbers for easy cross-referencing.
- Integrated Tools: Advanced software allows dynamic updates ensuring precision in matching metric and imperial parts.
- Compatibility Checks: Frequent audits ensure cross-reference systems maintain accurate compatibility across specifications.
| Method | Implementation | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Database Systems | Extensive setup | Accurate correlations |
| Software Integration | Ongoing updates | Dynamic adjustments |
| Audits & Checks | Regular assessments | Consistent compatibility |
Conclusion
Understanding both metric and imperial systems is crucial for ensuring compatibility and efficiency in global machinery setup.
Footnotes
1. Comparison of measurement standards in engineering. ↩︎
2. Guide to matching parts with global machinery specs. ↩︎
3. Online tools for metric to imperial engineering conversions. ↩︎
4. Importance of technical literacy in imperial drawing standards. ↩︎
5. Overview of CAD/CAM software with built-in conversion features. ↩︎
6. Understanding metric vs. imperial fastener standards and threading. ↩︎
7. Best practices for managing dual-system parts inventory. ↩︎
8. What Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) specifications mean for parts. ↩︎
9. Training resources for interpreting technical engineering blueprints. ↩︎
10. How part cross-referencing works in the aftermarket industry. ↩︎




