Excavator track chains are critical components of construction equipment, and choosing the right ones can be overwhelming. I’ve learned the hard way that missing a key parameter can lead to costly mistakes.
To ensure you’re getting the right track chains, confirm the following technical parameters: pitch measurement, link count, type of seal and lubrication, track shoe dimensions, and material composition. You also need compatibility with the machine’s make and model 1. Making the wrong choice can result in operational inefficiencies and damage to your equipment.
Confirming these parameters can seem tedious, but they are crucial for optimal performance and long-term reliability of your excavator. Let’s dive deeper into each parameter to ensure you make the right choice.
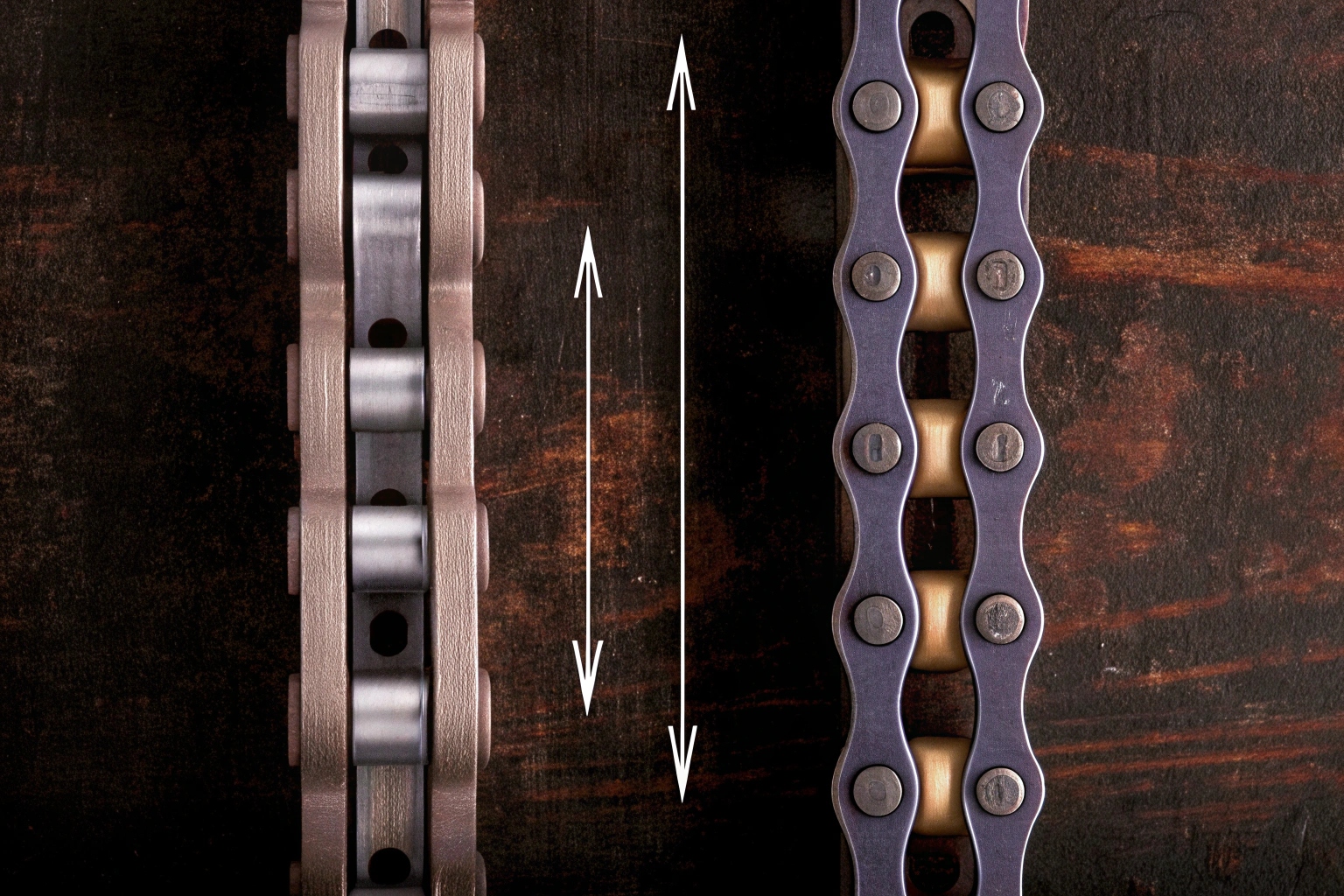
How do I measure my track pitch and bushing diameter?
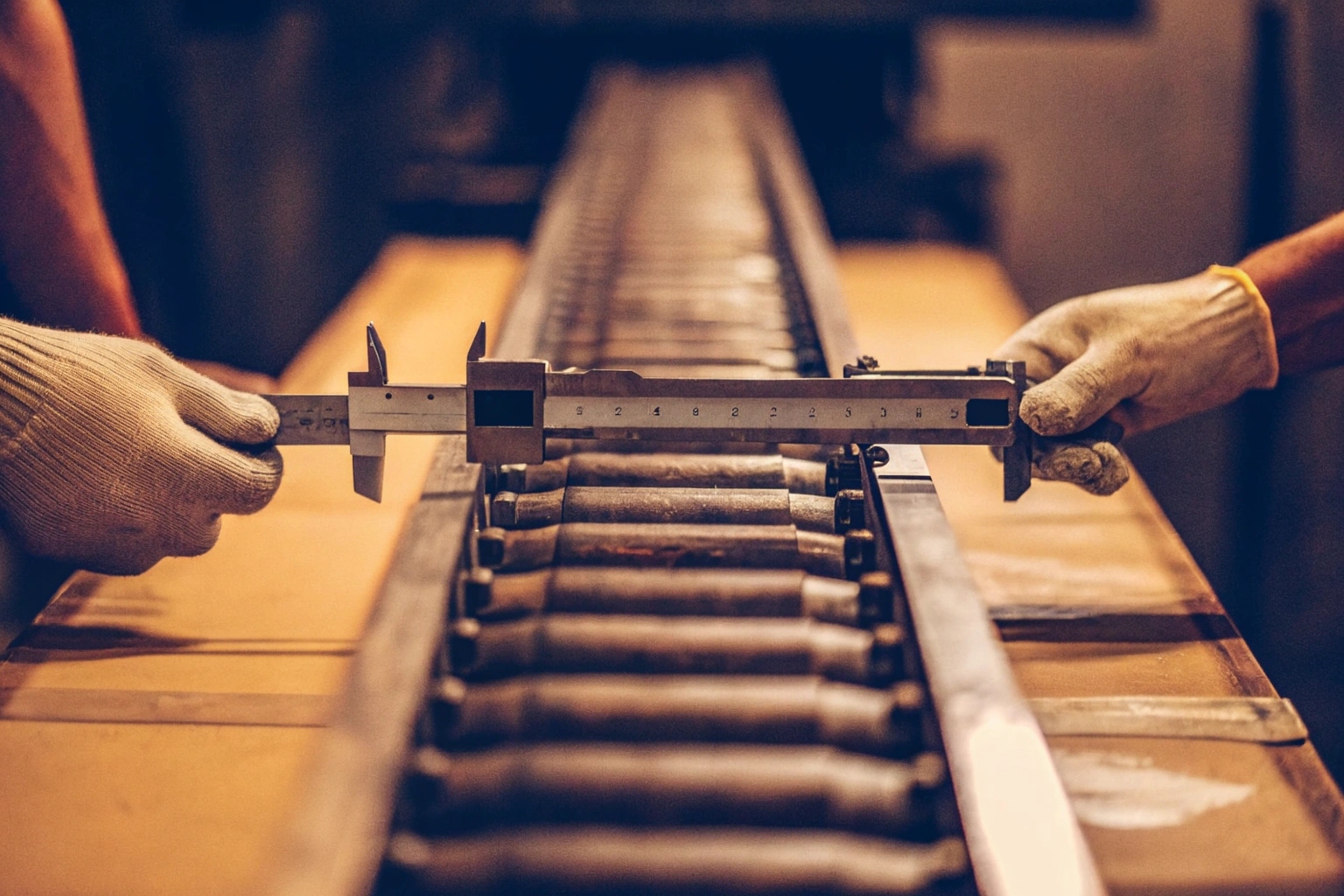
Measuring the pitch and bushing diameter can be a daunting task. When I first started, I often found myself second-guessing my measurements, which could lead to mismatched parts and frustrating delays.
To measure track pitch, calculate the distance between the centers of two consecutive pins in the chain. Similarly, for the bushing diameter 2, measure the external diameter of the bushing, ensuring it aligns with the sprocket and link rail height. This ensures smooth operation without any fitment issues.
Understanding the mechanics of measurement is key. Track pitch and bushing diameter are pivotal in ensuring a perfect fit with the sprocket. Mismatched sizes can result in operational hiccups and early component wear. Here’s a breakdown to aid understanding:
Key Pitch Sizes
| Description | Common Sizes (mm) |
|---|---|
| Standard Pitch | 152 – 228.6 |
| Heavy Duty Pitch | 260 |
| CAT 329D Pitch | 171.45 |
Importance of Precision
Precision in measurement cannot be overstated. A small error can cause the chain to fit poorly, disrupting the machine’s balance and performance. Here’s a checklist for accurate measurement 3:
- Use a reliable measuring tape or caliper.
- Measure multiple times to verify consistency.
- Cross-reference measurements with manufacturer specifications.
Proper measurement also ensures that the parts will not wear prematurely, avoiding the hassle and expense of frequent replacements.
Should I choose sealed or SALT chains for my applications?
Selecting between sealed 4 and SALT chains 5 has always intrigued me. Each has its strengths, and the decision often depends on one’s working environment and specific needs.
Sealed chains are typically preferred for applications where minimal maintenance is desired, as they are designed to keep contaminants out. In contrast, SALT (Sealed and Lubricated Track) chains incorporate a lubrication barrier, offering extended wear life, particularly in harsh conditions.
Understanding the conditions you’re working in is critical for this decision:
Sealed Chains
- Best for: Cleaner environments with minimal debris.
- Maintenance: Lower, but may wear faster in gritty areas.
SALT Chains
- Best for: Heavy-duty, dusty, or muddy work sites.
- Maintenance: Slightly higher upfront but typically offers longer performance life.
Decision Matrix
| Feature | Sealed Chains | SALT Chains |
|---|---|---|
| Environment Suitability | Clean | Harsh |
| Maintenance Required | Lower | Moderate |
| Longevity | Moderate | High |
By aligning the type of chain with your application, you ensure operational efficiency and longevity, catering to specific environmental challenges.
What track shoe width fits my ground conditions?
Selecting the right track shoe width involves more than just matching specs. I recall underestimating this factor and ended up with a setup that constantly got bogged in soft terrain.
The width of your track shoe 6 impacts the machine’s ground pressure. Wider shoes offer better support in soft soils, while narrower shoes provide stability and traction on harder surfaces.
It’s important to match track shoe width with your specific ground conditions:
Understanding Terrain Needs
- Soft and Wet Terrain: Choose wider shoes to distribute weight and reduce the risk of getting stuck.
- Hard and Rocky Terrain: Opt for narrower shoes for increased pressure and grip.
Configuration Analysis
| Ground Condition | Recommended Shoe Width |
|---|---|
| Muddy, soft surfaces | Wide (e.g., 900mm) |
| Hard, compact surfaces | Narrow (e.g., 600mm) |
Practical Considerations
Take into account both your typical operating conditions and any seasonal changes that might affect the terrain. It’s often beneficial to have track shoes suited for multiple conditions if the nature of your work changes frequently.
How do I specify master link type and pin retention?
Specifying master link type 7 and pin retention 8 can often seem like a minor detail. But I’ve found these components critical for ensuring the longevity of the track chain.
A proper master link maintains chain integrity, facilitating easy assembly and disassembly. Similarly, the method of pin retention ensures the chain’s stability during operation.
Choosing Master Links
Considerations: The choice often depends on your assembly requirements and disassembly frequency. Options vary from split links to solid links, each offering a balance between ease of maintenance and robust performance in demanding conditions.
Pin Retention Methods
| Type | Longevity | Ease of Installation |
|---|---|---|
| Split Pin | Moderate | Easy |
| Bolt-On | High | Moderate |
Importance in Applications
A well-specified master link and pin can significantly ease maintenance routines and improve the overall durability of the track chain.
Conclusion
Making informed decisions on excavator track chains ensures reliability and efficiency. Carefully consider each parameter for optimal equipment performance.
Footnotes
1. Model guides for ensuring seamless excavator fitment. ↩︎
2. Overview of bushing diameter measurements for chain alignment. ↩︎
3. Precise measurement techniques for optimal equipment fitting. ↩︎
4. Information on sealed chains in clean environments. ↩︎
5. SALT chain advantages in harsh working conditions. ↩︎
6. Importance of shoe width selection for diverse terrains. ↩︎
7. Comprehensive guide on master link types and uses. ↩︎
8. Effective pin retention methods for chain durability. ↩︎